IoT Batch Jobs: Uses, Trends & Best Practices - Your Guide!
Is the seamless orchestration of tasks across a multitude of devices within the Internet of Things (IoT) a reality, or a futuristic fantasy? Batch jobs on IoT devices are not just a concept; they are the engines driving efficiency, scalability, and intelligent automation in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
In the bustling world of interconnected devices, from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, the need to manage operations efficiently has never been more critical. Batch jobs provide a structured and streamlined approach to handle large volumes of data generated by these IoT devices, ensuring that tasks are executed in an orderly, automated manner. This approach significantly reduces the need for manual intervention, ultimately freeing up resources and minimizing the potential for human error. Think of it as a highly organized task force of digital assistants, each working in concert to achieve common goals.
Let's delve into the specifics of how this works, and why it matters. A batch job, at its core, represents the execution of a series of tasks or operations in a pre-defined, sequential manner. This sequential approach is the cornerstone of efficient data processing and control, especially when dealing with an array of devices generating constant streams of data. The power of batch jobs lies in their ability to automate complex processes, such as device updates, data analysis, and system configurations. When applied to IoT devices, this automation becomes a cornerstone of efficient management.
- Sophie Rain Takes On Spiderman Video Part 2 Unleashed
- Discover The World Of Cinema At Wwwmkvmoviespointcom
To fully grasp the potential, it's crucial to understand how to set up IoT devices to support these operations. This process involves several key steps, starting with ensuring the devices are properly configured to collect and transmit data as required. Data integrity is paramount, so the next step is to verify that these devices have stable, secure network connections to facilitate seamless data transfer. Ensuring data transfer is of paramount importance when the devices are expected to perform complex, critical tasks. If the connection is not stable then the data may not be correctly sent, if the connection is not secure the data could be compromised, which can lead to loss and other complications.
The practical application of batch jobs in the IoT sphere is diverse and far-reaching. From streamlining the firmware updates across a fleet of connected vehicles to coordinating data synchronization across smart city infrastructure, the applications are limitless. Consider, for instance, the remote management of a network of environmental sensors in a remote location. Through the use of batch jobs, administrators can schedule routine data collection, implement software updates, and monitor the devices health, all without having to physically visit the site. This level of remote management dramatically reduces operational costs and enhances efficiency.
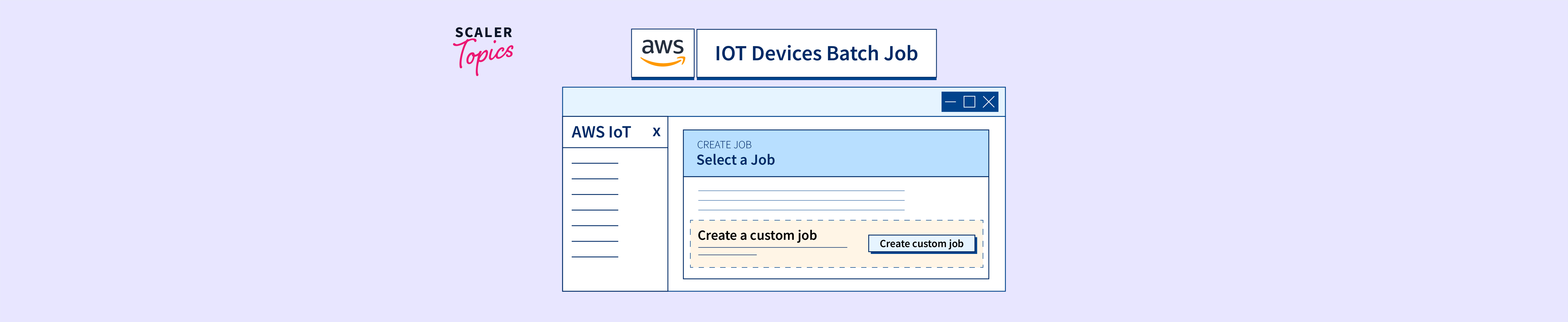
Azure and AWS IoT offer comprehensive tools that assist in scheduling and tracking such jobs that update millions of devices. Conceptually, a job wraps one of these actions and tracks the progress of execution against a set of devices. A device twin query defines the set of devices with which a job interacts. The ability to batch devices, defining how a job is applied to the devices within a group, further streamlines the process.
- Unveiling The Life Of Mellstroys Wife A Journey Of Love And Resilience
- Aubrey Wyatts Goodbye Letters A Journey Of Heartfelt Farewells
To gain a better understanding of how batch jobs operate, let's break down the key elements involved. A job's core components include a clear description of the task, the ID of the specific device group to which it applies, and the status of the job. The status can reflect various stages, from pending and running, to complete, cancelled, or failed. The ability to monitor the status in real time allows administrators to keep track of progress and make adjustments as needed. The ability to understand the device group to which the job is applied is crucial for target efficiency.
IoT device batch jobs are processes that handle large volumes of data generated by IoT devices in a structured and efficient manner. They empower businesses to make real-time data-driven decisions and optimize operations.
Let's consider some key use cases where IoT batch jobs truly shine:
- Firmware Updates: One of the most common uses is for firmware updates across a fleet of devices. This is especially important to improve security as security flaws are found and software needs to be kept up to date. The process is much more efficient than trying to update devices manually.
- Data Processing: Batch jobs are used to handle and process large datasets generated by IoT sensors and devices. This includes data aggregation, filtering, and transformation.
- Remote Configuration: Easily configure and deploy new configurations to devices, especially beneficial for settings such as network credentials, security settings, and software parameters.
- Scheduled Tasks: Automate the execution of tasks, such as data backups, system diagnostics, and device restarts, at specified times.
- Automated Diagnostics: Run diagnostic tests remotely and automate the repair of devices based on these tests.
- Security Measures: Batch jobs are used to apply security patches, enforce security policies, and regularly update security certificates across devices.
The implementation of these batch jobs requires a solid strategy. Consider these best practices for remote IoT batch job execution:
- Prioritize Security: Start with robust security measures to protect your devices and data from unauthorized access.
- Define Clear Objectives: Determine clear objectives for each batch job to ensure the desired outcomes.
- Thorough Testing: Before deployment, test batch jobs in a controlled environment.
- Implement Monitoring: Continuously monitor the execution of batch jobs.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select the right IoT platforms and tools that support batch job functionalities.
- Optimize Data Transfer: Consider optimizing data transfer to manage bandwidth and speed up the batch jobs.
- Error Handling: Design with error-handling mechanisms.
- Documentation: Maintain clear documentation for your batch jobs.
The ability to remotely monitor CPU, memory, and network usage, coupled with the capacity to receive alerts based on monitored IoT data and run batch jobs on devices, provides a comprehensive approach to managing IoT infrastructure. This approach offers the complete overview, giving an unprecedented level of control. This leads to the ability to act on events proactively instead of reactively.
The future of IoT batch job execution is poised for continued advancement. Future trends include:
- AI-Powered Automation: Integration of AI to optimize batch job scheduling, performance, and error handling.
- Edge Computing: Moving some batch job processing to the edge devices for faster responses and reduced latency.
- Enhanced Scalability: Ability to handle an ever-increasing number of devices and data volumes.
- Advanced Security: Greater focus on end-to-end security protocols for data protection.
- Integration with Cloud Services: Expanded integration with various cloud services for better data analysis, storage, and processing.
Essentially, an IoT device batch job is a process where multiple IoT devices work together to perform a set of predefined tasks in bulk, collaborating to complete projects without the need for constant human intervention. This team of digital robots, controlled remotely, represents the future.
Understanding batch jobs in the context of IoT devices is vital. Simply put, a batch job is a set of tasks or commands that are executed in sequence without user intervention. This automated execution model is the key to efficient management and operation of complex IoT systems. Its a strategic move, helping companies manage and control assets more efficiently. It is a crucial element for anyone looking to use IoT to its full potential.
Article Recommendations
- Discovering The World Of Mkvmovie Point Your Ultimate Movie Resource
- Discovering The Life Of Mellstroys Wife
Detail Author:
- Name : Mr. Emmett Gislason V
- Username : theodore65
- Email : adrien.will@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1995-10-30
- Address : 5566 Jordane Village Apt. 498 North Ashlychester, WY 68071-2425
- Phone : 1-575-628-5988
- Company : Stoltenberg, King and Stracke
- Job : Geological Sample Test Technician
- Bio : Porro quaerat qui praesentium. Animi at quod deleniti totam qui officia mollitia. Explicabo explicabo adipisci impedit voluptatem laboriosam sunt. Beatae explicabo sint odit non et.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/nikita_official
- username : nikita_official
- bio : Illo numquam dolorum fugiat enim fugit. Et quia harum excepturi cumque explicabo dolorum.
- followers : 1933
- following : 1564
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@eichmannn
- username : eichmannn
- bio : Dolorum dolore aut voluptatibus quia.
- followers : 2913
- following : 832
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/eichmann2025
- username : eichmann2025
- bio : Deserunt laudantium qui fugit nihil est facere.
- followers : 389
- following : 907
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/nikita1692
- username : nikita1692
- bio : Consectetur consectetur sed non saepe.
- followers : 1300
- following : 2011